Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure that involves reshaping or reducing the labia minora or labia majora. While some individuals consider this surgery for aesthetic preferences, others pursue it to address physical discomfort, medical concerns, or complications that affect daily function.
In Sydney, Dr Mark Kohout, a Specialist Plastic Surgeon, often consults with patients experiencing labial discomfort that may qualify for Medicare assistance. However, it is important to understand the strict criteria Medicare applies before funding this type of surgery.
This article outlines everything you need to know to determine whether your labiaplasty could be covered, and how to approach the process with realistic expectations.
What Is Labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure designed to change the size, shape, or symmetry of the labia, most often the labia minora. While it can be performed for cosmetic reasons, it is also sought by patients experiencing:
- Chronic irritation or pain during walking, cycling, or intercourse that interferes with comfort or limits daily activities. This can result from friction against clothing, prolonged sitting, or during specific movements.
- Hygiene difficulties caused by excess tissue, which can trap moisture and lead to recurrent infections such as yeast infections or bacterial imbalances. These issues may require frequent medical treatment.
- Discomfort in tight clothing or swimwear, where the labia may become visible or cause pressure that leads to embarrassment or discomfort during social and recreational activities.
- Physical interference with exercise or other activities, including challenges in performing exercises like running, pilates, or bike riding due to rubbing or pinching of the labial tissue.
- Asymmetry due to congenital conditions, hormonal influences, or childbirth-related trauma, which may create functional or aesthetic concerns that affect the patient’s self-perception and comfort.
Dr Mark Kohout, based in Sydney, frequently evaluates patients with such concerns to determine if their symptoms meet Medicare’s medical necessity criteria. Every case is unique, and understanding the distinction between aesthetic goals and medically justifiable symptoms is crucial.
Medicare and Labiaplasty: What You Need to Know
Medicare in Australia does not cover procedures performed purely for cosmetic reasons. However, it may provide rebates when labiaplasty is deemed medically necessary to treat or alleviate physical health concerns.
The key mechanism for coverage is the Medicare Benefits Schedule (MBS), which includes Item 35534 for labiaplasty under specific circumstances:
“Vulvoplasty or labioplasty, in a patient aged 18 years or more, performed by a specialist in the practice of the specialist’s specialty, for a structural abnormality that is causing significant functional impairment, if the patient’s labium extends more than 8 cm below the vaginal introitus while the patient is in a standing resting position.”
This item outlines measurable clinical criteria and requires supporting documentation to qualify. It is often reviewed on a case-by-case basis and assessed based on the severity of the symptoms and impact on the patient’s quality of life.
When Is Labiaplasty Considered Medically Necessary?
To qualify for Medicare coverage, labiaplasty must address clearly defined medical issues, including:
- Persistent physical discomfort during movement, exercise, or sexual activity that cannot be relieved through non-surgical management. The discomfort must be regular and significantly affect the patient’s ability to perform daily tasks.
- Recurrent infections, rashes, or dermatitis due to poor aeration or hygiene. Patients may experience frequent skin irritation, redness, or discharge, sometimes requiring antibiotic or antifungal medications.
- Functional interference, such as difficulty using tampons, wearing tight garments, or participating in sports. This may include inability to maintain normal hygiene routines or perform professional duties.
- Psychological distress directly tied to physical symptoms (to be documented by a healthcare provider), which may contribute to anxiety, embarrassment, or reduced quality of life, though not as a standalone justification for surgery.
In these situations, a medical practitioner must assess and verify that symptoms cause significant interference with daily life. Dr Mark Kohout, Plastic Surgeon in Sydney, conducts thorough assessments and works closely with referring GPs to determine if your condition meets the MBS criteria.
Understanding the Assessment Process
Navigating Medicare eligibility for labiaplasty involves several coordinated steps:
- Visit Your GP: Begin by discussing your symptoms. The GP will assess whether a referral to a Plastic Surgeon is warranted. They may ask you to describe when symptoms occur, their severity, and their impact.
- Obtain a Specialist Referral: A referral is necessary to consult an AHPRA-registered surgeon such as Dr Mark Kohout. Your GP will provide clinical notes and a summary of previous treatments.
- Clinical Evaluation: During your consultation, your specialist will:
- Examine anatomical features, noting measurements and potential abnormalities.
- Measure labial dimensions as per MBS criteria, including the 8 cm extension rule in a standing position.
- Document symptoms and their severity, ensuring a record of how these symptoms affect function.
- Record past treatment attempts, such as prescriptions or physiotherapy reports.
- Formal Diagnosis and Report: Your surgeon will issue a clinical report to support a Medicare claim if eligibility is established. This may be requested with photographic evidence, measurements, and medical history if there is an audit.
This process ensures transparency and adherence to Medicare guidelines.
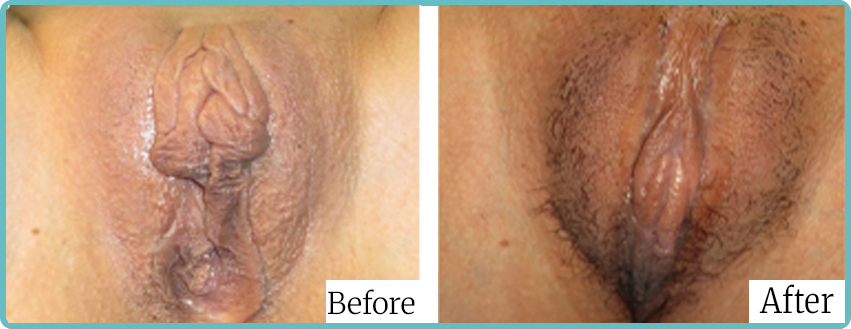
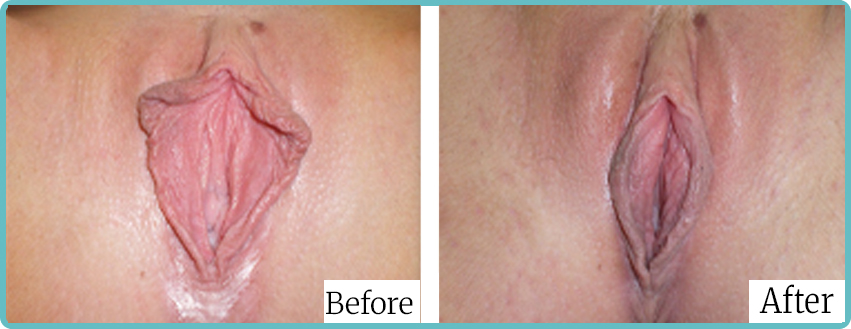
Labiaplasty Surgery Before and After Images
What Medicare May Cover
If your procedure meets the criteria for Item 35534, Medicare may contribute to part of the surgeon’s fee and anaesthetic costs, based on the MBS rebate. Medicare does not cover private hospital admission fees; however, an eligible MBS item number may allow you to claim benefits from your private health insurer if you hold appropriate hospital cover.
Post-operative reviews for up to eight weeks are generally included in the surgeon’s fee at no additional charge. Patients should request a detailed written estimate to understand all expected costs.
Private Health Insurance and Additional Costs
Even when Medicare and an applicable item number apply, out-of-pocket expenses are still common in private hospitals. Private health insurance may reduce some of these costs, depending on your level of cover. Key considerations include:
- Hospital excess: A fixed amount payable on admission before your insurer contributes.
- Gap fees: Any difference between surgeon or anaesthetist fees and the combined Medicare/insurance rebate.
- Theatre and facility charges: Significant costs associated with private hospitals; Medicare does not cover these.
- Medications and post-surgical garments: Items such as pain relief, antibiotics, and compression garments are generally not covered by Medicare or private insurance.
Always confirm waiting periods, exclusions, and rebate limits with your insurer. Patients with top-tier hospital cover may receive higher benefits and face fewer out-of-pocket expenses.
FAQs About Medicare and Labiaplasty in Australia
Can my symptoms be assessed as medically necessary if they vary in severity throughout the month?
Yes, fluctuating symptoms can still meet Medicare’s criteria if they cause functional impairment. Documenting patterns over time, including menstrual cycle-related changes, can support your case during clinical assessment.
Does labiaplasty eligibility differ for patients with congenital versus acquired conditions?
Medicare eligibility is based on the presence of significant functional impairment, regardless of whether the condition is congenital or acquired (e.g., post-childbirth changes). Both must meet the same clinical standards.
Will photographs or measurements be part of the evaluation process for Medicare claims?
Yes. Clinical documentation may include labial measurements and photographs to support the assessment against Medicare’s anatomical criteria. These are handled with strict privacy and ethical care.
Is psychological discomfort alone considered a valid reason for Medicare coverage?
Psychological distress must be linked to physical symptoms to be considered under Medicare. Emotional wellbeing is important, but documentation must demonstrate a physical component affecting function.
Can I still explore Medicare coverage if previous treatments helped temporarily but symptoms returned?
Yes, Medicare considers cases where non-surgical treatments were initially effective but later became insufficient. It’s important to document the full treatment history and symptom progression.
Are there differences in eligibility if labial hypertrophy is bilateral versus affecting one side only?
No. Whether the condition affects one or both sides, eligibility depends on the presence of functional symptoms and the anatomical threshold set by the MBS. Both can be assessed equally.
What type of documentation should I bring to my consultation with a Plastic Surgeon?
Bring any relevant medical records, referral letters, history of infections, symptom journals, and past treatment details. These materials help the surgeon evaluate your case thoroughly and provide accurate clinical support for Medicare assessment.
Medical References
- Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery: A Review – Journal of Women’s Health – https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/jwh.2019.7944
- The Safe Practice of Female Genital Plastic Surgery – PMC – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8263325/
- Labiaplasty Minora Reduction – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448086/
- Female Genital Mutilation and Reconstructive Surgery – Journal of Clinical Medicine – https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/9/10/3333
- Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery: A Systematic Review – Journal of Sexual Medicine – https://www.jsm.jsexmed.org/article/S1743-6095(20)30141-4/
- Reconstructive Surgery for Female Genital Mutilation – Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery – https://www.jprasurg.com/article/S1748-6815(20)30035-6/
- Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery: A Review of the Literature – Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy – https://journals.lww.com/jwhpt/Fulltext/2020/01000/Female_Genital_Cosmetic_Surgery__A_Review_of_the.5.aspx
The Role of Your Plastic Surgeon
A Specialist Plastic Surgeon, such as Dr Mark Kohout in Sydney, plays a vital role in supporting Medicare eligibility. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting an accurate, respectful examination that takes into account the patient’s comfort and privacy while evaluating physical indicators.
- Ensuring that the patient’s condition is assessed against MBS criteria, including documentation of all measurements and symptoms.
- Providing a clinical diagnosis that supports medical necessity, which may include symptom diaries, photographic records, and treatment history.
- Preparing reports and working with Medicare and private insurers as required, including managing appeals, submitting forms, and responding to queries.
Next steps with Dr Mark Kohout in Sydney, NSW
If you experience concerns and would like to discuss possibilities with Dr Kohout, the first step is to visit your GP for assessment and referral.
You can then arrange a consultation with Dr Mark Kohout, Specialist Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon (FRACS) in Sydney, NSW, for an individual evaluation and discussion of whether your condition may meet Medicare’s criteria for consideration.
Further Reading
- Read more about Genital Surgery In Sydney
- Read more about Hymen Repair Sydney
- Read more about Vaginoplasty Sydney
- Read more about Return To Exercise After Labioplasty
Related Blog Posts
Medicare for Breast Lift – Mastopexy
A breast lift, also known as mastopexy, is a surgical procedure designed to reshape and lift the breasts, also addressing the contour. While many associate this procedure with cosmetic alterations,…
Can I have a Hernia Repair…
Dr Mark Kohout and His Experience in Hernia Repair Surgery Dr Mark Kohout is a plastic and reconstructive surgeon based in Australia, with extensive experience in performing a variety of…
FAQs about Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck Surgery)…
Abdominoplasty, commonly referred to as a tummy tuck, is a surgical procedure to remove excess skin and fat from the abdomen and tighten the underlying muscles. When combined with BodyTite and Morpheus8, you can…

Experienced Plastic Surgeon
Dr. Mark Kohout
A qualified plastic surgeon who operates with care and integrity, based in central Sydney with over 20 years of experience in the cosmetic field. His extensive training and experience assures patients they are in highly trained surgical hands. Dr. Kohout is a dedicated, friendly professional who is committed to providing the high quality care, support and results, alongside his compassionate team.
Dr Mark Kohout (MED0001133000)
Specialist Plastic Surgeon
Specialist registration in Surgery – Plastic Surgery