Effective Strategies for Managing Scars After Gynaecomastia Surgery
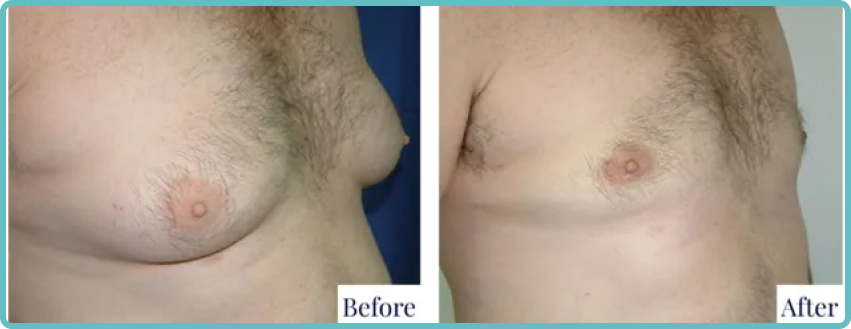
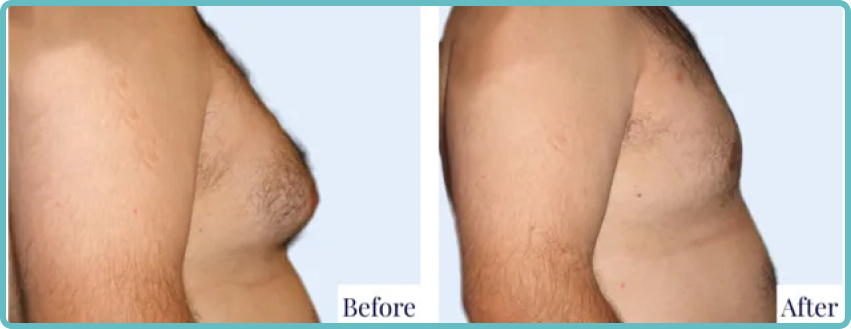
Gynaecomastia, a condition characterised by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, affects many men worldwide. While surgical intervention can effectively address this condition, the resulting scars are a common concern for patients. This blog post aims to provide a thorough understanding of gynaecomastia scars and offer practical advice on their management.
Understanding Gynaecomastia and Its Treatment
Gynaecomastia is a benign enlargement of male breast tissue, which can occur in one or both breasts. It’s a common condition that can affect males of all ages, from newborns to elderly men. The causes are varied and can include hormonal imbalances, certain medications, medical conditions, and obesity.
For many men, gynaecomastia can be a source of discomfort, both physical and emotional. When conservative treatments prove ineffective, surgical intervention may be recommended. The two primary surgical approaches are:
-
- Liposuction: This technique is used when the enlargement is primarily due to excess fatty tissue.
- Excision: This method is employed when glandular tissue or excess skin needs to be removed.
In some cases, a combination of both techniques may be necessary to achieve the desired results.
Types of Scars from Gynaecomastia Surgery
The nature and extent of scarring following gynaecomastia surgery depend on various factors, including the surgical technique used, the amount of tissue removed, and individual healing characteristics. Common types of scars include:
- Periareolar Scars: These scars encircle the areola, either partially or completely. They’re often used in cases where glandular tissue needs to be removed.
- Inframammary Fold Scars: Located in the natural crease beneath the breast, these scars are typically used in cases requiring skin removal.
- Lateral Chest Wall Scars: These small scars are usually the result of liposuction and are positioned on the side of the chest.
- Combination Scars: In some cases, a combination of the above scar types may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome.
Factors Influencing Scar Formation
Several factors can influence how scars form and heal following gynaecomastia surgery:
- Genetics: Some individuals are predisposed to forming more noticeable scars.
- Age: Younger skin typically has better elasticity and healing capacity.
- Skin Colour: Darker skin tones may be more prone to hyperpigmentation or keloid formation.
- Surgical Technique: The skill of the surgeon and the techniques used can significantly impact scar formation.
- Post-operative Care: Proper wound care and following post-operative instructions are crucial for optimal healing.
- Tension on the Wound: Excessive tension can lead to wider, more noticeable scars.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports better wound healing.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can impair healing and lead to more noticeable scars.
Immediate Post-operative Care
Proper care in the immediate post-operative period is crucial for minimising scar formation and promoting optimal healing. Here are some key points to consider:
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere strictly to your surgeon’s post-operative instructions.
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently clean the incision sites as directed by your surgeon to prevent infection.
- Avoid Strain: Refrain from heavy lifting or strenuous activities that could put tension on the healing wounds.
- Wear Compression Garments: These can help reduce swelling and support the healing tissues.
- Attend Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups allow your surgeon to monitor your healing progress and address any concerns promptly.
- Be Patient: Healing takes time, and it’s normal for scars to appear more prominent initially before improving.
Long-term Scar Management Strategies
Once the initial healing phase is complete, typically after about six weeks, you can begin to implement more proactive scar management strategies:
-
- Silicone-based Products: Silicone sheets or gels have been shown to improve the appearance of scars. They work by hydrating the scar tissue and regulating collagen production.
- Massage: Gentle massage of the scar tissue can help soften and flatten scars. Use a moisturising cream or oil and apply gentle pressure in circular motions.
- Sun Protection: UV exposure can cause scars to darken and become more noticeable. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF to the scar area when exposed to sunlight.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams containing ingredients like vitamin E, allantoin, or onion extract may help improve scar appearance, although scientific evidence for their efficacy is mixed.
- Hydration: Keep the scar well-moisturised to maintain skin elasticity and prevent the scar from becoming dry or itchy.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and E, zinc, and protein can support ongoing skin health and healing.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall skin health and can contribute to better scar healing.
Advanced Scar Treatment Options
For scars that remain prominent despite conservative management, several advanced treatment options are available:
-
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can help reduce inflammation and flatten raised scars.
- Laser Therapy: Various types of lasers can be used to address scar texture, colour, and overall appearance.
- Microneedling: This technique involves creating tiny punctures in the skin to stimulate collagen production and improve scar appearance.
- Chemical Peels: These can help manage skin texture and reduce discolouration associated with scars.
- Cryotherapy: For raised scars, freezing the scar tissue can help flatten it.
- Scar Revision Surgery: In some cases, surgical revision of the scar may be considered to address its appearance.
It’s important to note that these advanced treatments should only be performed by qualified healthcare professionals and are typically considered only after conservative measures have been exhausted.
When to Seek Professional Help
While most scars improve with time and proper care, there are situations where you should seek professional medical advice:
- Signs of Infection: Redness, warmth, increased pain, or discharge from the incision sites.
- Excessive Scarring: If scars become raised, red, or extend beyond the original incision lines.
- Persistent Pain: Ongoing discomfort or pain in the scar area beyond the expected healing period.
- Functional Impairment: If the scar is causing restriction in movement or other functional issues.
- Emotional Distress: If concerns about your scars are causing significant anxiety or affecting your quality of life.
Further Reading about Male Breast Revision with Sydney Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Mark Kohout
- Read more about Dr. Mark Kohout’s Procedure Page on Gynaecomastia
- Read more about Dr. Mark Kohout’s Resources Page on Risks and Complications of Plastic Surgery
- Read more from Dr. Mark Kohout’s Blog on Gynaecomastia and Chest Correction for Men with Male Breasts
Related Blog Posts
FAQs of Abdominoplasty after Weight Loss…
Abdominoplasty after significant weight loss can help individuals address the excess skin and increase the visibility of muscle tone that often results from substantial weight reduction. In Australia, many people…
Techniques in Tummy Tuck – Abdominoplasty:…
Popular Abdominoplasty Techniques in 2025 The field of tummy tuck – abdominoplasty surgery continues to advance, offering patients diverse options. In this blog, Sydney Plastic Surgeon Dr Mark Kohout will discuss some of the…
Breast Reduction Medicare Cover – Will…
Will Medicare Cover My Breast Reduction? Breast reduction, medically known as reduction mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure that removes excess breast tissue and skin to achieve a breast size more…

Experienced Plastic Surgeon
Dr. Mark Kohout
A qualified plastic surgeon who operates with care and integrity, based in central Sydney with over 20 years of experience in the cosmetic field. His extensive training and experience assures patients they are in highly trained surgical hands. Dr. Kohout is a dedicated, friendly professional who is committed to providing the high quality care, support and results, alongside his compassionate team.
Dr Mark Kohout (MED0001133000)
Specialist Plastic Surgeon
Specialist registration in Surgery – Plastic Surgery